From waste to energy
Waste-to-energy plants burn municipal solid waste (MSW), to produce steam in a boiler that is used to generate electricity. MSW is a mixture of energy-rich materials such as paper, plastics, wood.
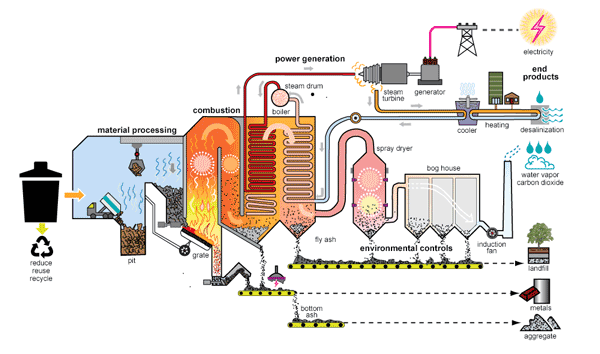
There are different types of waste-to-energy systems or technologies. The most common type used is the mass-burn system, where unprocessed MSW is burned in a large incinerator with a boiler and a generator for producing electricity (see illustration below). Another less common type of system processes MSW to remove most of incombustible materials to produce refuse-derived fuel (RDF).
First The process of generating electricity in a mass-burn waste-to-energy plant has seven stages:
Second Waste is dumped from garbage trucks into a large pit.
Third A giant claw on a crane grabs waste and dumps it in a combustion chamber.
Fourth The waste (fuel) is burned, releasing heat.
Fifth The heat turns water into steam in a boiler.
Sixth The high-pressure steam turns the blades of a turbine generator to produce electricity.
Seventh An air pollution control system removes pollutants from the combustion gas before it is released through a smoke stack.
Eighth Ash is collected from the boiler and the air pollution control system.
Meet the solution owner
